RESPIREASY-DEDAKJ Prevention of Respiratory Diseases
The user is asking about the role of the RESPIREASY oxygen concentrator in the prevention of respiratory diseases. First, I need to confirm the basic functions of the RESPIREASY oxygen concentrator, which is usually used to provide oxygen to help improve hypoxia. Next, the prevention of respiratory diseases may involve how to prevent the onset of diseases through oxygen therapy, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, etc.
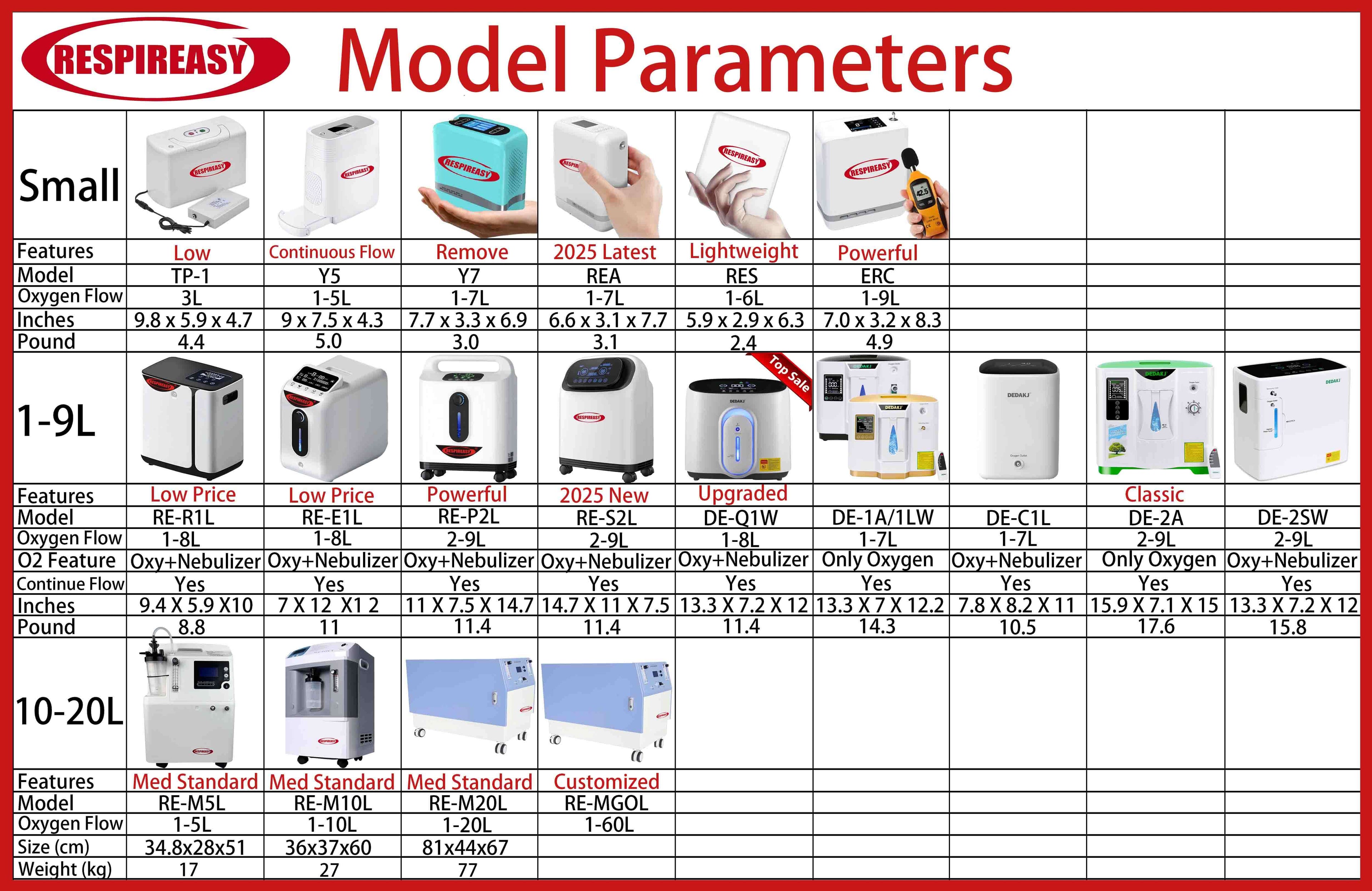
RESPIREASY-DEDAKJ home oxygen concentrator
RESPIREASY portable oxygen concentrator
RESPIREASY medical oxygen concentrator
First, you should understand the specific application scenarios of oxygen concentrators in prevention. For example, for patients with chronic respiratory diseases, long-term home oxygen therapy (LTOT) is a common treatment method that may help prevent worsening of the disease. In addition, for high-altitude areas or places with severe air pollution, oxygen concentrators may be used for daily oxygen supplementation, enhance lung function, and prevent hypoxia-related problems.
Then, you need to consider the user's possible deep needs. Users may want to know how oxygen concentrators can specifically help with prevention, such as how to use it, who is suitable for it, and what to pay attention to. It may also be necessary to distinguish between prevention and treatment. Oxygen concentrators play more of an auxiliary role in prevention, such as improving hypoxia and enhancing immunity, rather than directly treating diseases.
So the answer can only be based on general knowledge of oxygen concentrators. It is necessary to mention the applicable population, such as patients who need oxygen therapy recommended by doctors, and the use of healthy people in specific environments, but emphasize that it cannot replace medical advice and should be followed.
In addition, preventive measures may include combining the use of oxygen concentrators with maintaining good living habits, such as quitting smoking, air circulation, and proper exercise. The correct use and maintenance of oxygen concentrators are also important, such as regular cleaning and checking of equipment performance to avoid risks caused by improper use.
It needs to be clearly structured and explained in points, such as applicable scenarios, prevention mechanisms, usage recommendations, precautions, etc. The language should be easy to understand and suitable for mobile phone reading, avoid too many professional terms, and ensure that the information is accurate, reminding users to use it under the guidance of a doctor, especially the use of medical equipment must be cautious.
Regarding the role of RESPIREASY oxygen concentrator in respiratory disease prevention, combined with the general functions of oxygen concentrators and medical knowledge of respiratory disease prevention, the following is a specific analysis:
1. The relationship between the core functions of RESPIREASY oxygen concentrators and respiratory disease prevention
The main function of the oxygen concentrator is to separate and enrich oxygen in the air through physical means (such as molecular sieve technology) to provide users with oxygen concentrations higher than the ambient concentration (usually 28%-90% adjustable). In respiratory disease prevention, its core value is reflected in the following aspects:
1. Improve hypoxia and enhance lung compensation
- For patients with chronic respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, and pulmonary fibrosis, long-term low-flow oxygen inhalation (follow doctor's advice) can relieve fatigue and dyspnea caused by hypoxia and reduce the risk of acute attacks.
- For healthy people in severe air pollution (such as PM2.5 exceeding the standard), high-altitude hypoxic environment or excessive fatigue, short-term oxygen inhalation can reduce the burden on the lungs and prevent respiratory stress response caused by hypoxia.
2. Assisting the recovery of respiratory diseases and reducing the recurrence rate
- For patients in the recovery period of pneumonia, bronchitis, etc., oxygen support can accelerate tissue repair, enhance immunity, and reduce the recurrence of the disease caused by hypoxia.
2. Applicable population and prevention scenarios
1. People who are medically recommended to require oxygen therapy
- For patients diagnosed with COPD, interstitial lung disease, etc. and with arterial oxygen partial pressure (PaO₂) ≤55 mmHg, long-term home oxygen therapy (LTOT) is the standard treatment for preventing the deterioration of the disease (≥15 hours per day).
- Patients with sleep apnea syndrome (combined with hypoxemia) can use oxygen inhalation while using a ventilator to improve nocturnal hypoxia and reduce the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications.
2. Health protection scenarios
- Air pollution/haze days: Using an oxygen concentrator indoors can increase the local oxygen concentration and reduce respiratory mucosal damage caused by inhalation of pollutants.
- Before/during high-altitude travel: Oxygen inhalation in advance can prevent altitude sickness (such as headaches and pulmonary edema), especially for those with weak cardiopulmonary function.
- Occupationally exposed population: Workers who are exposed to dust and chemical gases for a long time can use oxygen as an additional protective measure (with professional protective equipment).
III. Scientific use recommendations (prevention-oriented)
1. Follow the principle of "preventive oxygen therapy"
- Non-disease population: Only use it for a short period of time (30-60 minutes each time, 1-2 times a day) when there are clear symptoms of hypoxia (such as shortness of breath, dizziness) or in high-risk environments, and avoid over-reliance.
- Chronic disease population: Must strictly follow the doctor's advice to formulate an oxygen inhalation plan (flow rate, duration), and regularly check blood oxygen saturation (SpO₂ maintained at 90%-94%).
2. Combined with lifestyle adjustments
- Keep indoor ventilation and use air purifiers to reduce pollutant inhalation;
- Quit smoking, avoid secondhand smoke, and reduce respiratory irritation;
- Moderate breathing training (such as abdominal breathing) to enhance lung function.
3. Equipment maintenance and safety
- Clean the oxygen inhalation pipeline and humidification bottle regularly to prevent bacteria from breeding and causing respiratory infections;
- Keep away from fire sources (oxygen helps combustion) and keep the environment dry and ventilated during storage.
IV. Precautions (avoid misunderstandings)
1. Cannot replace basic preventive measures
- The oxygen concentrator is an auxiliary tool and cannot directly "prevent" the occurrence of diseases. Vaccination (such as influenza and pneumonia vaccines), healthy diet, and regular exercise are still the core prevention methods.
2. Use with caution in non-indication groups
- Long-term high-concentration oxygen inhalation (>40%) by healthy people may cause oxygen poisoning (such as lung damage and retinopathy). Children and pregnant women need to consult a doctor before use.
3. Choose compliant products
- Confirm that the RESPIREASY oxygen concentrator has a medical device registration certificate to avoid using unlicensed "health-care" equipment to ensure that the oxygen concentration and flow rate are accurately controllable.
Summary
RESPIREASY oxygen concentrator plays a role in respiratory disease prevention mainly by improving the hypoxic environment, assisting rehabilitation, and responding to high-risk scenarios. It is especially suitable for patients with chronic respiratory diseases and health protection in specific environments. However, it should be noted that:
- Disease prevention needs to be combined with medical guidance to avoid blind use;
- The use of equipment is aimed at "correcting hypoxia" rather than a universal means of "improving health level";
- Regular communication with doctors and adjustment of plans according to individual conditions can safely and effectively play the role of prevention.